The Differences and Similarities of Restorative Justice and Mediation
By: JJ Durham, Oct 2018 (updated on 12/11/25 by Rebecca Taplin)
Conflict is a natural part of human relationships, yet few of us are ever taught effective conflict resolution skills. When tensions escalate, many people turn to mediation, and entire industries exist to help disputing parties work through their differences with the support of a neutral facilitator. But mediation is only one pathway. An alternative approach, the restorative approach, centers the relationship itself—ensuring that every person involved is treated with dignity, listened to fully, and given space to share how they have been affected. This restorative model broadens the focus beyond just solving the problem to repairing harm, rebuilding trust, and supporting the well-being of everyone involved.
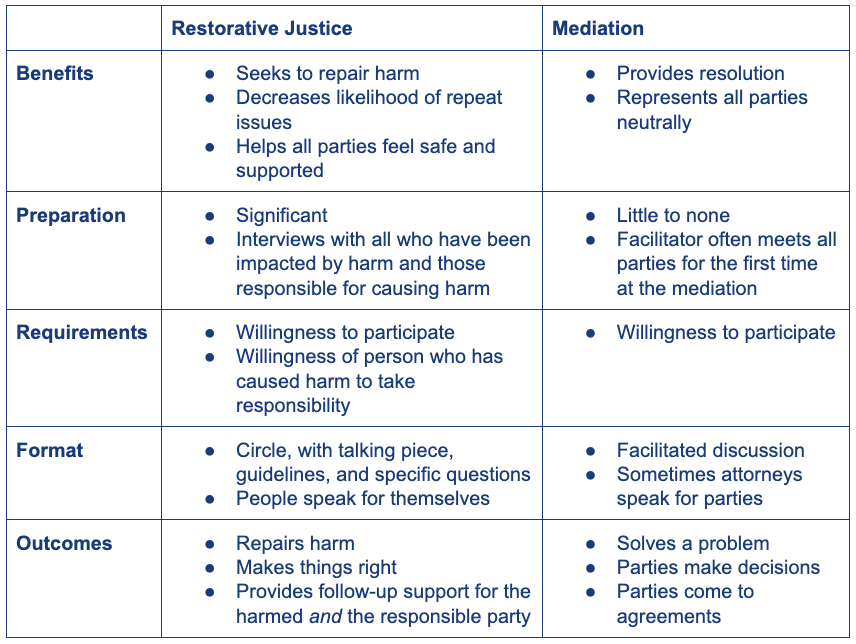
Mediation is a process where disputing parties use a neutral third party to facilitate a dialogue about their dispute. The process is usually voluntary and the parties remain in control of the outcome. The focus is on problem solving and the mediator assists the parties by clarifying concerns and interests, defining and framing issues, relaying information and helping the parties generate solutions. The goal is a “win win” and/or a negotiated agreement with which the parties can live. Mediation is used commonly to resolve housing and small claims disputes.
Restorative Justice is a process where a person who has been harmed and the person who has harmed come together with others who have been affected to discuss what happened, what the impact has been, and what can be done to repair the harm. The process requires the person who has harmed to take responsibility. It also requires the harmed party to be willing to engage to some extent with the person who caused them harm. The focus is to repair the harm and satisfy the needs of the person who has been harmed and others who have been affected. Restorative Justice is often used as a pre-arraignment alternative process in a criminal matter, but can be (and is) used in companies, organizations, and educational settings.
The skill sets for practitioners of both processes greatly overlap. Furthermore, both Restorative Justice and Mediation practitioners use a specific process in their work. And both Restorative Justice and Mediation practice encourages respectful dialogue and listening.
Restorative Practices have grown from the ideas of Restorative Justice and are often used in schools to build community and create a more restorative/less punitive environment for students and teachers. They are also used in community organizations, faith-based groups, and even corporate settings. Contact us to learn more about how P2RC can help resolve conflicts in your setting.
If you’re looking for a conflict resolution process whose focus is to repair the harm and not just find a solution the parties can live with, Restorative Justice Practices provide the clearest pathway forward.